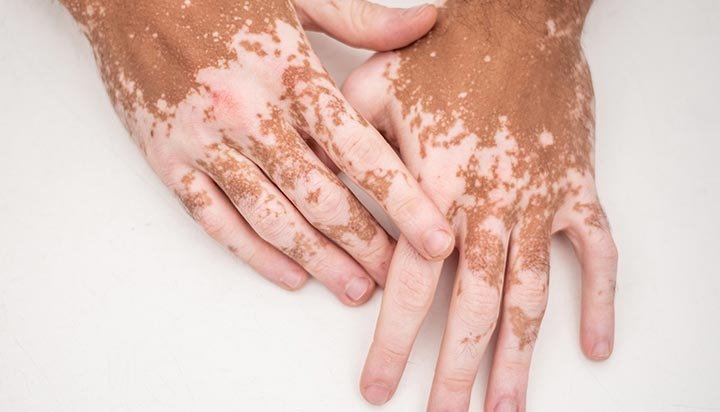
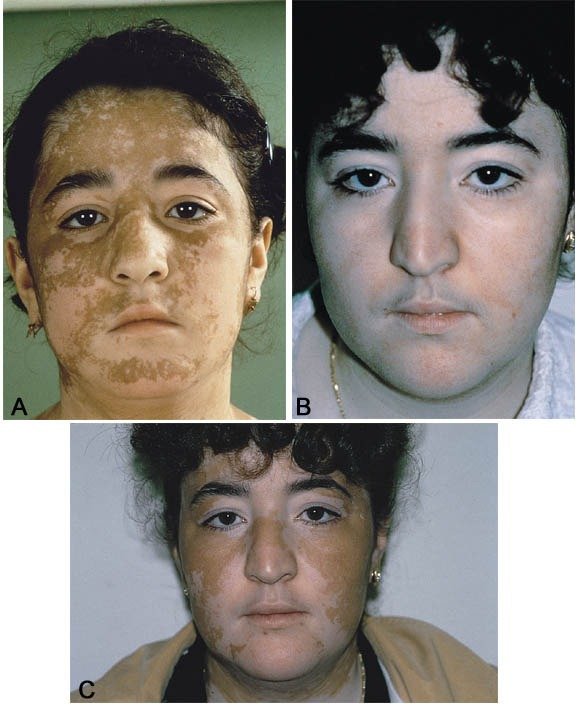
Vitiligo can present in many forms, but in advanced cases with widespread pigment loss, repigmentation therapies may no longer provide satisfactory results. In such situations, monobenzone cream may be used as part of permanent depigmentation therapy to achieve a more even skin tone.
This article explains when monobenzone is considered, how it works, and what patients should understand before starting treatment.
Why Depigmentation Is Considered in Extensive Vitiligo
When vitiligo affects a large percentage of the body, remaining pigmented areas can appear patchy and cosmetically distressing. Depigmentation therapy aims to lighten the remaining normal skin so that overall tone becomes more uniform.
Depigmentation is typically considered when:
- Vitiligo affects more than 50% of the body
- Repigmentation therapies have failed
- The condition has been stable for years
- The patient understands the irreversible outcome
This approach focuses on appearance and quality of life rather than restoring pigment.

How Monobenzone Works on Pigment Cells
Monobenzone causes permanent destruction of melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin. Unlike skin-lightening agents, its effects are irreversible and progressive.
Its action includes:
- Gradual loss of pigment in treated areas
- Immune-mediated melanocyte destruction
- Permanent depigmentation over time
Because of this mechanism, monobenzone must be used with extreme care and only for approved medical indications.
According to DermNet NZ, monobenzone is indicated exclusively for permanent depigmentation in patients with extensive vitiligo and should never be used for cosmetic skin lightening.
How Monobenzone Is Applied
Depigmentation with monobenzone is a gradual process that may take several months.
General use principles:
- Apply once or twice daily to pigmented areas only
- Avoid already depigmented skin
- Use strict sun protection
- Monitor progress regularly
Sun exposure can cause severe sunburn in depigmented skin, making daily sunscreen essential.
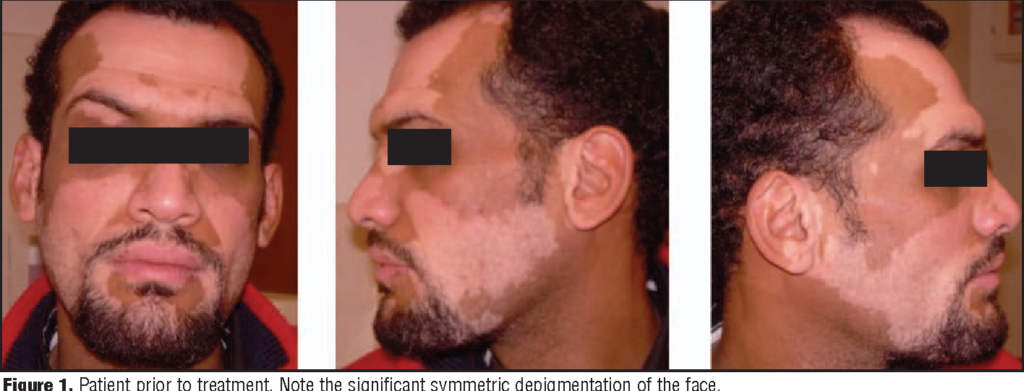

Possible Side Effects and Considerations
Because depigmentation is permanent, side effects can be both physical and psychological.
Possible risks include:
- Uneven depigmentation
- Skin irritation or contact dermatitis
- Increased photosensitivity
- Emotional adjustment to permanent skin color change
Thorough counseling before treatment is critical.
Choosing a Monobenzone Product
Formulation consistency is essential for predictable depigmentation. A commonly used medical-strength option is:
👉 monobenzone 20% cream
https://okdermo.com/product/benoquin-monobenzone-20-cream/
This concentration is typically used in supervised depigmentation protocols.
Who Should Not Use Monobenzone?
Monobenzone is not suitable for:
- Mild or localized vitiligo
- Cosmetic skin lightening purposes
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Patients unwilling to accept permanent depigmentation
A dermatologist must evaluate suitability before treatment begins.
Conclusion
Monobenzone plays a specific and important role in the management of advanced vitiligo when repigmentation is no longer effective. By allowing uniform depigmentation, it can significantly improve cosmetic appearance and patient confidence.
Because of its irreversible effects, monobenzone should always be used with full medical guidance and realistic expectations.